In an era increasingly defined by environmental awareness and the imperative for sustainable practices, biodegradable food containers have emerged as a beacon of hope for a greener future. These containers represent a significant stride towards reducing the ecological footprint of the foodservice industry, which has long been associated with excessive plastic waste and environmental degradation. The adoption of biodegradable food containers marks a departure from traditional plastics, notorious for their persistence in the environment and detrimental impact on ecosystems. Made from materials such as compostable plastics, plant fibers, and even seaweed-based compounds, these containers offer a viable alternative that breaks down naturally over time, significantly reducing their environmental impact. One of the primary advantages of biodegradable food containers lies in their ability to decompose into non-toxic components. Unlike conventional plastics that fragment into microplastics, which pose a severe threat to marine life and ecosystems, biodegradable materials degrade into organic matter or harmless substances.
This characteristic not only mitigates environmental pollution but also supports the transition towards a circular economy where waste is minimized, and resources are reused. Moreover, biodegradable containers often exhibit comparable performance to their plastic counterparts in terms of durability and functionality. The biodegradable food containers are designed to withstand various temperatures and conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of culinary applications, from takeout containers to disposable cutlery. This versatility ensures that businesses can maintain operational efficiency without compromising their commitment to sustainability. The growing popularity of biodegradable food containers is also driven by consumer demand for eco-friendly alternatives. As awareness of environmental issues intensifies, consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on the sustainability credentials of products. Restaurants, cafes, and food vendors are responding to this shift by embracing biodegradable options, thereby enhancing their brand reputation and appealing to a conscientious customer base. Furthermore, the production of biodegradable containers typically involves lower carbon emissions compared to traditional plastics. Many biodegradable materials originate from renewable resources, such as cornstarch or sugarcane, which require less energy to cultivate and process.
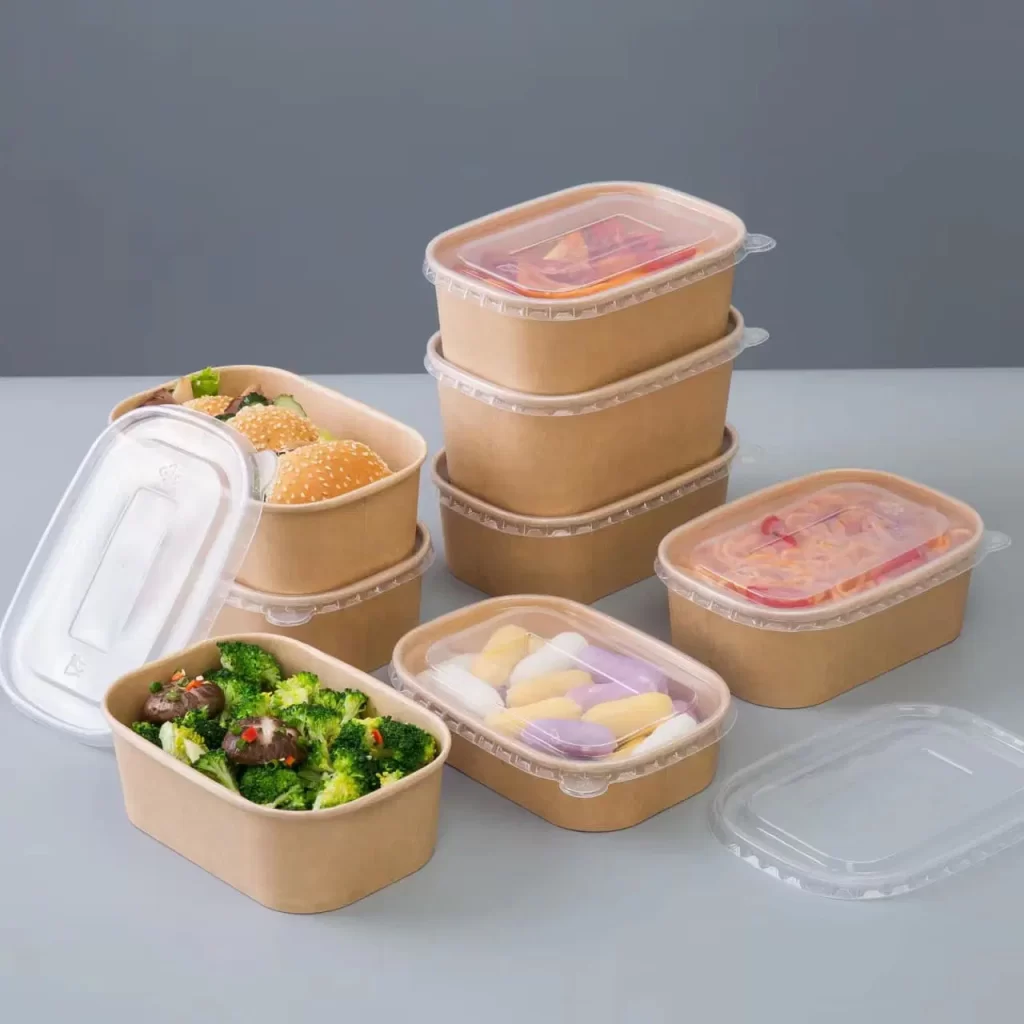 This aspect further contributes to reducing the overall carbon footprint of the food packaging industry, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change. Despite these benefits, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of biodegradable food containers. Issues such as cost competitiveness, availability of suitable recycling infrastructure, and misconceptions about biodegradability versus compostability need to be addressed. Industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers, must collaborate to overcome these barriers and promote the transition towards sustainable packaging solutions. Looking ahead, the future of biodegradable food containers appears promising, driven by continuous innovation and heightened environmental consciousness. Research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the efficiency and scalability of biodegradable materials, ensuring they meet rigorous standards for safety, functionality, and environmental impact. By reducing reliance on conventional plastics and promoting the use of renewable, biodegradable materials, businesses and consumers alike can contribute to a healthier planet for future generations. As these containers continue to gain traction globally, they embody a vision of a circular economy where every product is designed with the environment in mind a vision essential for building a sustainable future.
This aspect further contributes to reducing the overall carbon footprint of the food packaging industry, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change. Despite these benefits, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of biodegradable food containers. Issues such as cost competitiveness, availability of suitable recycling infrastructure, and misconceptions about biodegradability versus compostability need to be addressed. Industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers, must collaborate to overcome these barriers and promote the transition towards sustainable packaging solutions. Looking ahead, the future of biodegradable food containers appears promising, driven by continuous innovation and heightened environmental consciousness. Research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the efficiency and scalability of biodegradable materials, ensuring they meet rigorous standards for safety, functionality, and environmental impact. By reducing reliance on conventional plastics and promoting the use of renewable, biodegradable materials, businesses and consumers alike can contribute to a healthier planet for future generations. As these containers continue to gain traction globally, they embody a vision of a circular economy where every product is designed with the environment in mind a vision essential for building a sustainable future.